According to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc., the global CNC machine market is expected to grow to $100.9 billion by 2025. The industry is evolving rapidly using new technologies designed to increase precision, increase efficiency, reduce cycle time, and reduce waste.
Here is an overview of five machining trends that we believe strongly impact the market.
1. Everything is Becoming Smart
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is connecting the factory floor and is gathering real-time data about the environment, performance, efficiency, and health of each and every process. CNC machines are already smart thanks to CNC software. By adding a sensor and connecting it to the factory floor or internet, CNC machines will generate real-time data on the status of the equipment, productivity levels, efficiency, and energy usage – all of which impact your profitability. Here are a few things you can do with data IIoT data collected from CNC machinery.
- Receive a notification on your smart phone or tablet that a particular machine vibration levels are exceeding thresholds or operating temperatures are higher than normal – meaning it needs maintenance now – avoiding unexpected downtime.
- Know your exact production rates at any given second.
- Automatically power down equipment when not in use to save on energy costs.
- Understand exact power requirements for fabricating particular components
- Detect when parts are near end of life
2. Greater Part Complexity
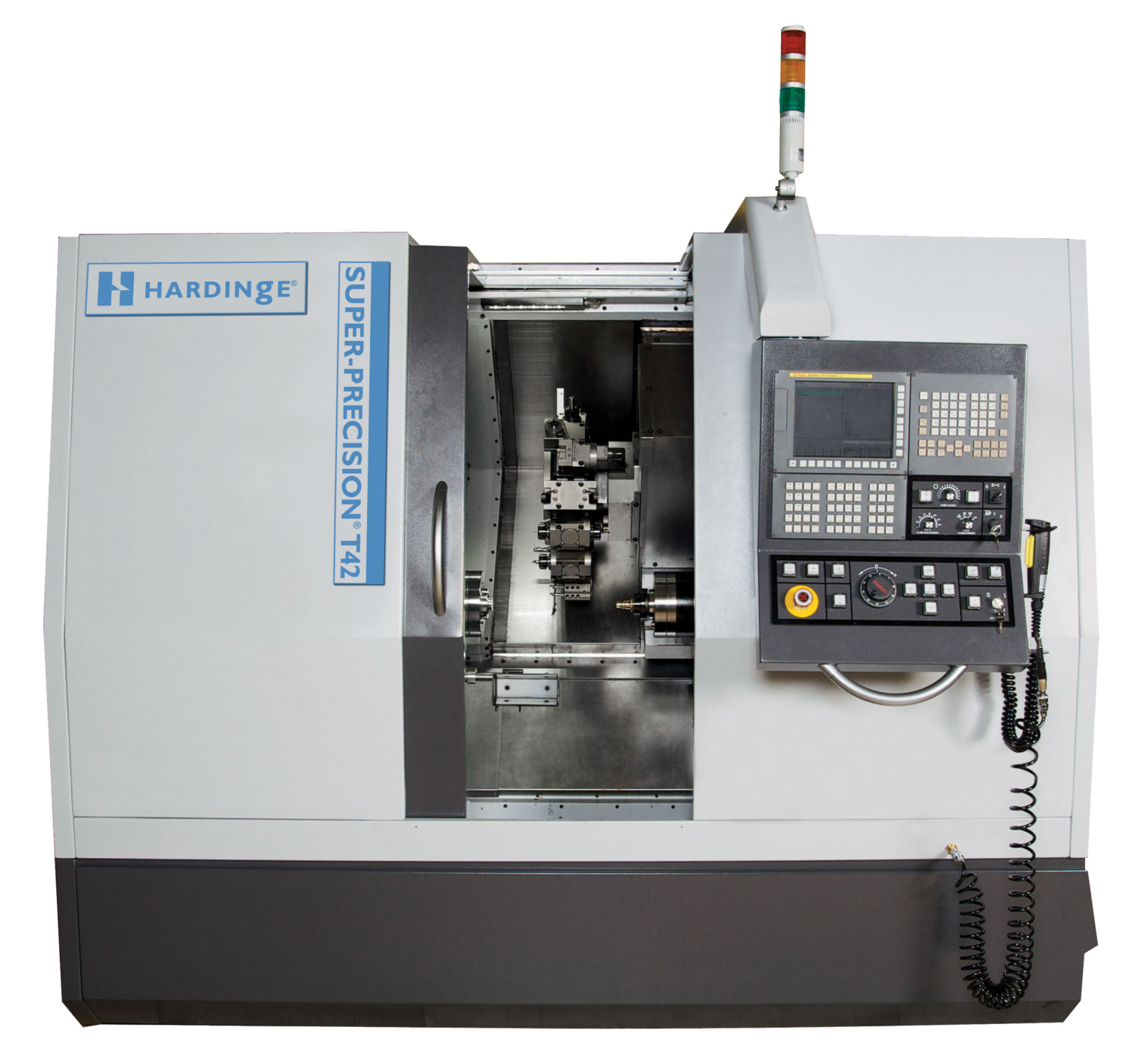
As technology and design advance in aerospace, automotive, medical, and the defense industries, there is an increasing need to cost-effectively manufacture more complex parts of various sizes and finishes, such as wind turbine blades. This is driving manufacturers like Hardinge to continue to innovate in all areas to meet the demand for more accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency.
To learn more about how these industries are meeting the demand for accuracy, download the eBook below.
3. More Accurate and Repeatable Precision
The market is demanding tighter tolerances, and more consistent quality and flexibility. New efficient product designs require extremely complex and tight-tolerance components for accuracy, safety, and optimal performance. New challenges arise with increasingly complex geometries and tough-to-machine materials that are lighter and stronger and require tools that can machine at the highest possible levels of accuracy and productivity.
Super precision machining with turning accuracy of 1–2 μm is becoming the new normal. Just to provide perspective on how precise this is — a human red blood cell is .7 μm.
Learn more about Hardinge SUPER-PRECISION® Offerings
4. The Rise of Multi-Axis Machining
The popularity of CNC machines that can perform more than three axes of movement (greater than just the three linear axes X, Y, and Z) is on the rise. Today, tooling can move across nine different axes, allowing for the machining of more intricate, precise, and delicate parts.
Although 5 -axis machining has been around for a while, it is experiencing new popularity, particularly in aerospace and defense applications. These markets are experience significant growth. For example, the commercial aircraft order backlog is at its peak of more than 14,000—with about 38,000 aircraft expected to be produced globally over the next 20 years (Source: Deloitte).
Learn More about Hardinge 5-Axis Machines
5. Quick-Change Workholding becomes Standard
Because complex parts often need to be run in small to medium sized lots, the changeover from one part to another has to be performed quickly without sacrificing quality. Quick-change technology has evolved to the point where it is very viable in everyday production. Adoption of quick-change workholding has accelerated and in 2019 is now is considered a standard practice in many shops.